VITAMIN b1
Ingredient
What is vitamin B1
Where does it come from?
Why is it used?
What are the benefits?
Bibliography
What is vitamin B1?
Thiamine: An Essential Vitamin
Thiamine is an essential nutrient that all body tissues need to function properly. Thiamine is the first B vitamin that scientists discovered. That is why its name bears the number 1. Like other B vitamins, thiamin is water soluble. This means that it dissolves in water and is not stored in your body, so you need to consume it regularly.
In fact, your body can only store about 20 days of thiamine at any given time. (Hammond et al., 2013)
Where does it come from?
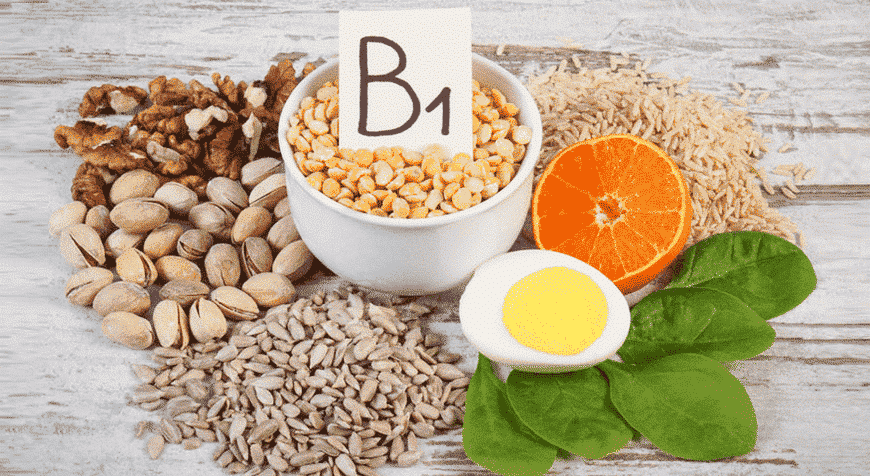
The richest food sources are sunflower seeds and wheat germ (Martel et al., 2022) Fortunately, thiamine is found naturally in a variety of foods and is added to others through the enrichment. It is also commonly added to multivitamins or taken as an individual supplement or as part of a B vitamin complex.
Why is it used?
Thiamine is a vitamin your body needs for cell growth, development, and function, as well as for turning food into energy (Office of Dietary Supplements – Thiamin, nd) B1 (thiamin). Thiamine plays an essential role in metabolism by helping to convert nutrients into energy.
A thiamine deficiency can impact many functions in your body, including those of the…:
- The nervous system
- Heart
- Brain
Thiamine is an essential nutrient necessary for the proper functioning of all tissues in the body.
You can find it in:
- Food
- Food supplements
- Multivitamins
Discover other plants used in our products
Bibliography
- Hammond, N., Wang, Y., Dimachkie, MM, & Barohn, RJ (2013). Nutritional Neuropathies. Neurologic Clinics, 31(2), 477-489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ncl.2013.02.002
2. Martel, JL, Kerndt, CC, Doshi, H., & Franklin, DS (2022). Vitamin B1 (Thiamin). In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482360/
3. Office of Dietary Supplements—Thiamin. (nd). Retrieved June 2, 2022, from https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/thiamin-healthprofessional/

